队列-先入先出(FIFO)的数据结构
队列的定义
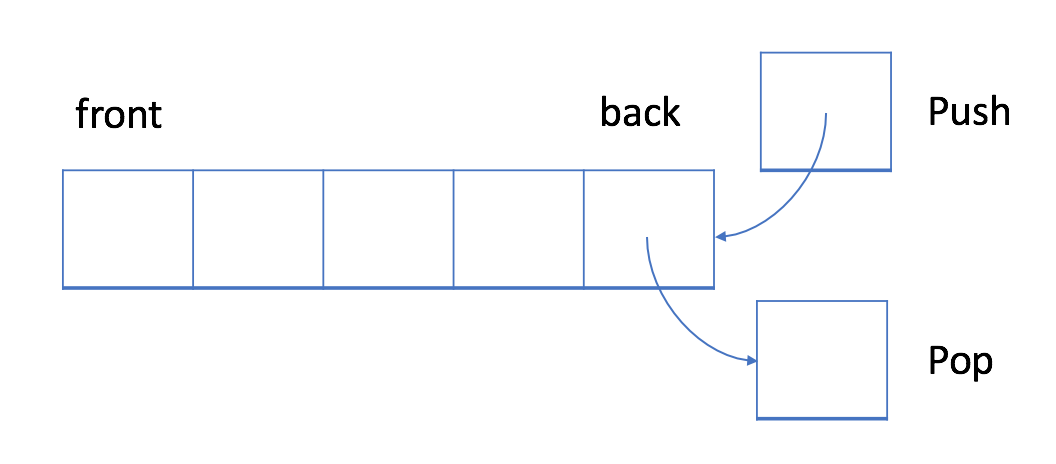
队列是指允许在一端进行插入,而在另一端进行删除的线性表.允许进行删除运算的一端成为队头(或排头),允许进行插入运算的一端称为队尾.
队列称为"先进先出"或"后进后出"的线性表.
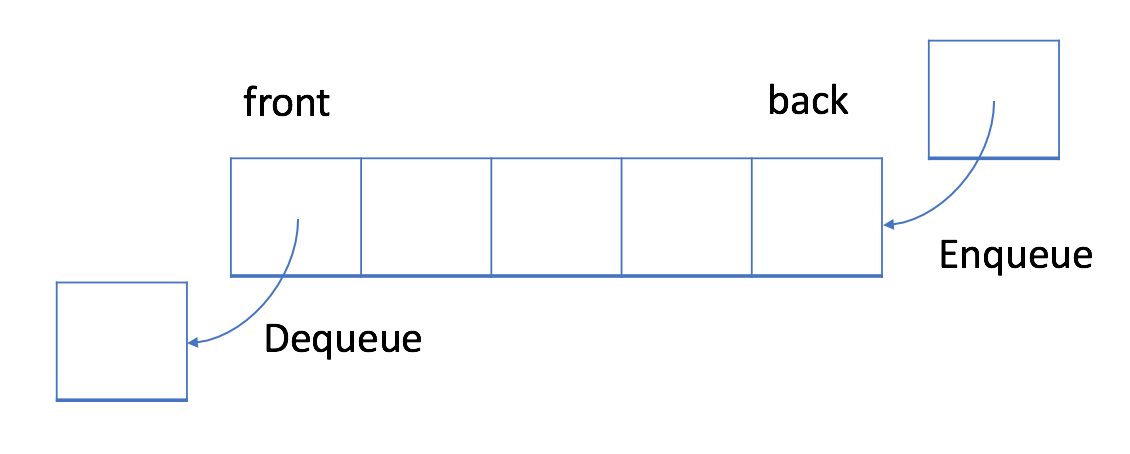
在 FIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素。
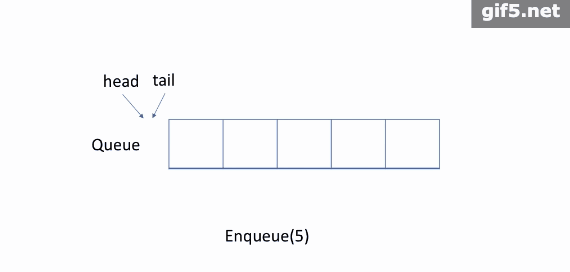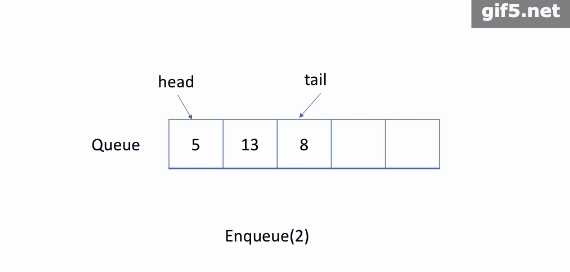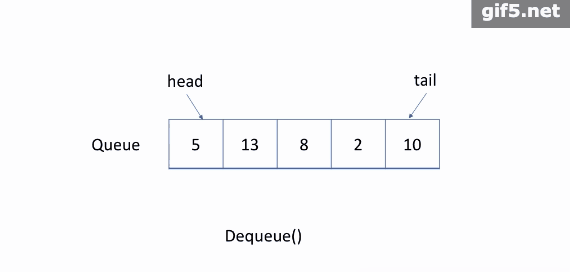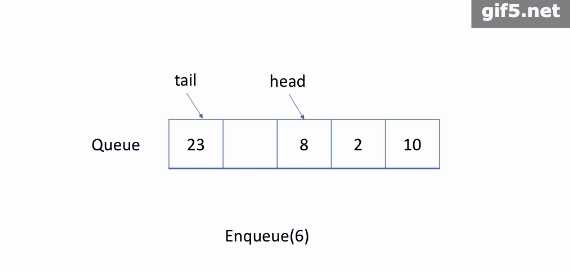
如上图所示,队列是典型的 FIFO 数据结构。插入(insert)操作也称作入队(enqueue),新元素始终被添加在队列的末尾。 删除(delete)操作也被称为出队(dequeue)。 你只能移除第一个元素。
示例 - 队列
1. 入队:您可以单击下面的 Enqueue 以查看如何将新元素 6 添加到队列中。
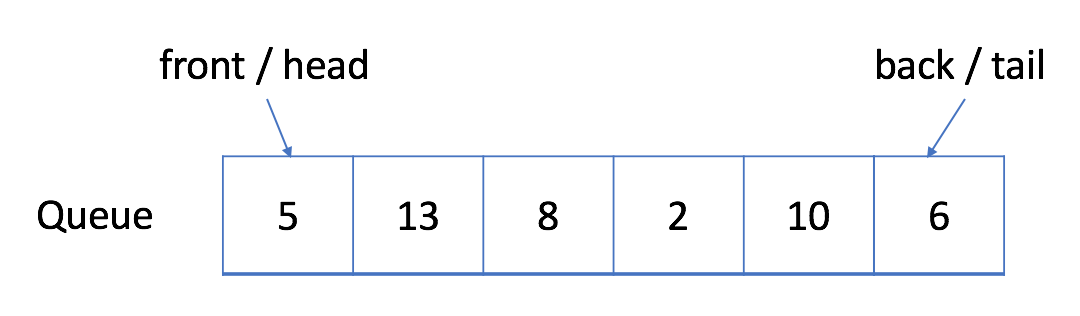
2. 出队:您可以单击下面的 Dequeue 以查看将删除哪个元素。

为了实现队列,我们可以使用动态数组和指向队列头部的索引。
如上所述,队列应支持两种操作:入队和出队。入队会向队列追加一个新元素,而出队会删除第一个元素。 所以我们需要一个索引来指出起点。
这是一个供你参考的实现(C++):
1 |
|
缺点
上面的实现很简单,但在某些情况下效率很低。 随着起始指针的移动,浪费了越来越多的空间。 当我们有空间限制时,这将是难以接受的。
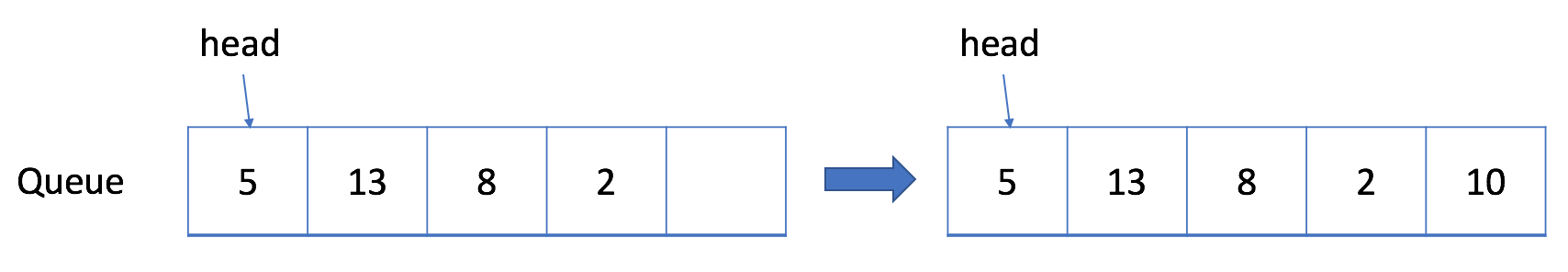
让我们考虑一种情况,即我们只能分配一个最大长度为 5 的数组。当我们只添加少于 5 个元素时,我们的解决方案很有效。 例如,如果我们只调用入队函数四次后还想要将元素 10 入队,那么我们可以成功。
但是我们不能接受更多的入队请求,这是合理的,因为现在队列已经满了。但是如果我们将一个元素出队呢?
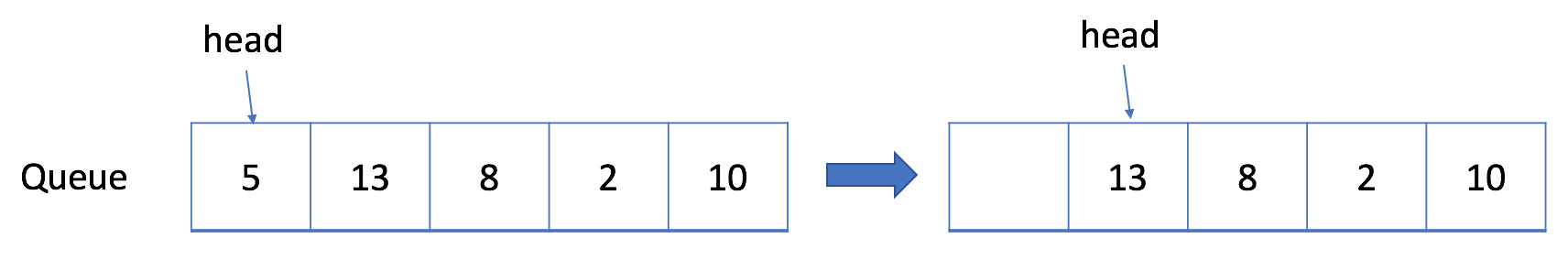
实际上,在这种情况下,我们应该能够再接受一个元素。
循环队列
此前,我们提供了一种简单但低效的队列实现。
更有效的方法是使用循环队列。 具体来说,我们可以使用固定大小的数组和两个指针来指示起始位置和结束位置。 目的是重用我们之前提到的被浪费的存储。
让我们通过一个示例来查看循环队列的工作原理。 你应该注意我们入队或出队元素时使用的策略。
仔细检查动画,找出我们用来检查队列是空还是满的策略。
栈-后入先出(LIFO)的数据结构
栈的定义
栈(Stack)是一种特殊的线性表,它所有的插入与删除都限定在表的同一端进行,允许插入与删除的一端称为栈顶,不允许插入与删除的一端称为栈底,当栈中没有元素时,称为空栈.
在 LIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的最新元素。
与队列不同,栈是一个 LIFO 数据结构。通常,插入操作在栈中被称作入栈 push 。与队列类似,总是在堆栈的末尾添加一个新元素。但是,删除操作,退栈 pop ,将始终删除队列中相对于它的最后一个元素。
示例 - 栈
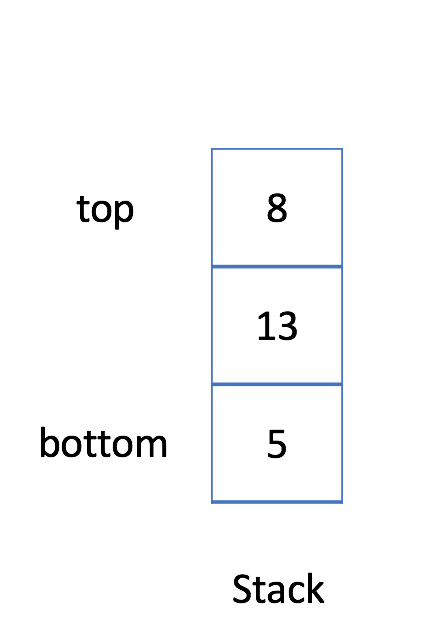
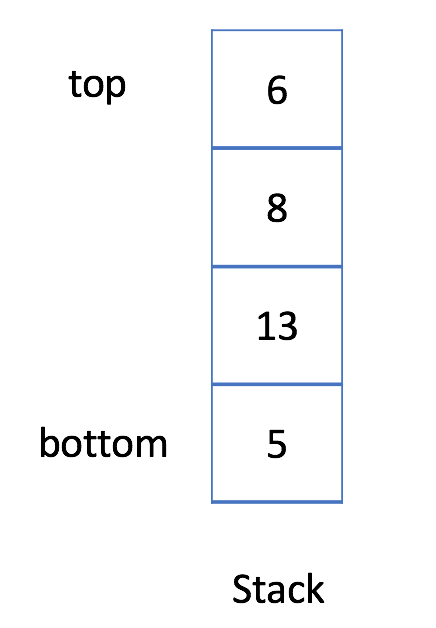
1. 入栈:你可以单击下面的 Push 按钮查看如何将新元素 6 添加到栈中。
2. 退栈:你可以单击下面的 Pop 按钮查看当你从栈中弹出一个元素时将移除哪个元素。
实现 - 栈
栈的实现比队列容易。动态数组足以实现堆栈结构。这里我们提供了一个简单的实现供你参考(C++):
1 |
|